Algorithms | Merge Sort In JavaScript
Table Of Contents
In previous articles we have covered Bubble Sort and Quick Sort and found out that the first one is the slowest one and is mainly used for educational purposes.
The latter is fast and efficient, but has a significant disadvantage - the complexity of O(N2) if the pivot element is wrongly chosen.
As we are beginning to find out, there is no such thing as a perfect sorting algorithm, each one has its own advantages and disadvantages.
Today we will learn Merge Sort, an algorithm that was invented by John von Neumann in 1945 and see how it works in practice.
The Definition
Merge sort is an efficient sorting algorithm that follows the "divide-and-conquer" approach.
It works by dividing the unsorted list by n sublists, each containing one element and repeatedly merging these sublists, producing new sorted sublists until one left.
This one is considered sorted.
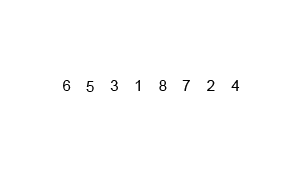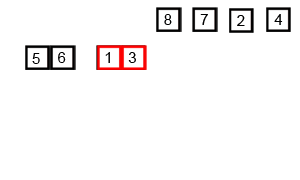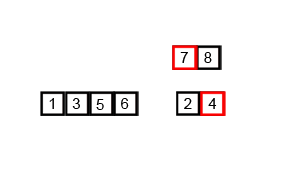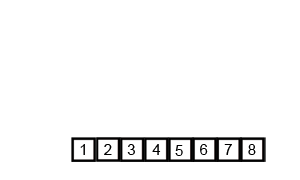
The visualization:

The Complexity
Best-case performance - O(NlogN).
Worst-case performance - O(NlogN).
Average - O(NlogN).
Pros And Cons
Merge Sort can be adapted to work with very large lists stored on media with slow-access speeds, such as disk storage or network-attached storage.
Pros
- The complexity of the worst, best and average case is
O(NlogN), which makes it very efficient - More efficient than Quick Sort for some types of lists if the data to be sorted can only be efficiently accessed sequentially (Linked Lists)
Cons
- May be slower than other sorting algorithms for small datasets
- The most common implementation requires the memory size of the input to be allocated for the sorted output to be stored in
Implementation In JavaScript
const merge = (left, right) => {
// The result will contain sorted array
let result = [];
// While there are items in arrays
while(left.length && right.length) {
// Check if the first left element is smaller than the first right
// If yes, throw to the sorted array and remove it
// If no, throw the first right element to the sorted array and remove it
if(left[0] < right[0]) {
result.push(left.shift());
} else {
result.push(right.shift());
}
}
// If anything left (one array is larger than another), concatenate it
return result.concat(left.slice().concat(right.slice()));
};
const mergeSort = arr => {
// If an array contains one or zero elements
// It is considered sorted
if(arr.length <= 1) {
return arr;
}
// Get the position of the element in the middle
const mid = Math.floor(arr.length / 2);
// Continuously cut array in half
// Until there is an array with one element left
const left = mergeSort(arr.slice(0, mid));
const right = mergeSort(arr.slice(mid));
// Merge two arrays back
return merge(left, right);
};Usage In JavaScript
// Assuming that the mergeSort function from the example above is accessible
const arr = [1, 23, 46, 12, 2, 3];
console.log(mergeSort(arr)); // Prints "[1, 2, 3, 12, 23, 46]"Summary
Merge Sort is an efficient sorting algorithm that is useful for sorting linked lists and large records.
Its average complexity is O(NlogN) and it produces a stable sort, which means that the same items in the original list retain their original positions in the sorted list.
Make sure to play with it and see you in the next article.